More about COVID-19 Airborne Transmission and Masks
This document of 29 March 2020 from the WHO discusses the various forms of infection transmission, concluding that there is unlikely to be a COVID-19 airborne transmission, but droplet transmission is common within close contact (within 1 m). Click here
This article dated 16 March 2020 concludes that airborne transmission may be possible, but not likely, and repeats the WHO instruction that COVID-19 does not require the wearing of masks.
This CDC Recommendation updated May 18, 2020 says "The contribution of small respirable particles, sometimes called aerosols or droplet nuclei, to close proximity transmission is currently uncertain. However, airborne transmission from person-to-person over long distances is unlikely."
If tiny drops generated from breathing and probably coughing containing coronavirus remain suspended for some time, then a face mask is both of use as protection against inhaling the virus and preventing spreading.
If the drops do not remain suspended for much time, a mask, especially a surgical mask will help stop a person with CO-19 from spreading, but is no protection to becoming infected, and could increase the chance of infection if the wearer adjusts the mask with contaminated fingers. Only a shield stops the wearer touching contaminated surfaces and then touching their face.
Medical personal in close contact with CO-19 patients must wear at least the N95 mask, plus a medically approved face shield.
If you're not sick but are around people who have the flu, wearing a surgical mask can help protect you from getting infected as long as it's tight-fitting. If there are gaps around the sides, then it's not helping much.
The only certain conclusion is that there is no certain conclusion yet. The WHO is slow on making any new recommendations.
Generation and Behavior of Airborne Particles (Aerosols) here.
Link to another report "Natural Ventilation for Infection Control in Health-Care Settings"
How long can virus live on surfaces?
Click her for WHO report "Is coronavirus spreading by talking and breathing?"
The WHO says "in an analysis of 75,465 COVID-19 cases in China, airborne transmission was not reported". However, this was before much was known about CO-19.
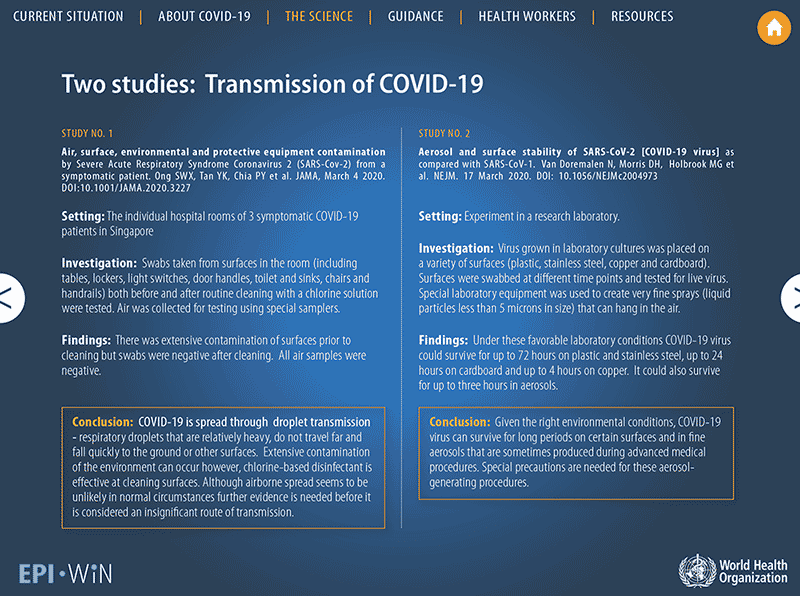
This is taken directly from a WHO report COVID-19 spreads through droplet transmission - respiratory droplets that are relatively heavy, do not travel far and fall quickly to the ground and other surfaces.
Extensive contamination of the environment can occur.
Although airborne spread seems to be unlikely in normal circumstances, further evidence is needed before it is considered an insignificant mode of transmission.
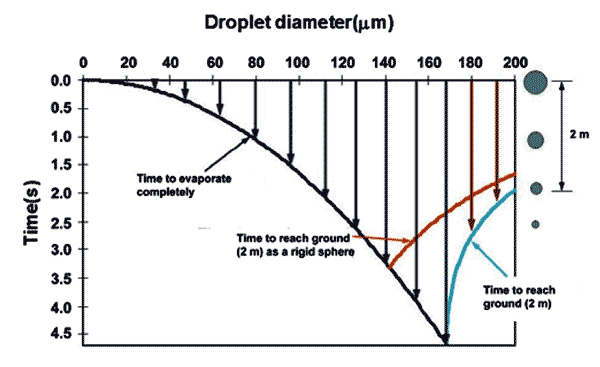 The Wells evaporation-falling curve of droplets
The Wells evaporation-falling curve of droplets
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, CDC is "additionally advising the use of simple cloth face coverings to slow the spread of the virus and help people who may have the virus and do not know it from transmitting it to others. Cloth face coverings fashioned from household items or made at home from common materials at low cost can be used as an additional, voluntary public health measure."
The CDC recommends wearing face masks in public settings to prevent spreading the disease, even though coronavirus airborne transmission is "unlikely."
A CDC report that virus droplet nuclei aerosols can stay suspended in the air during medical procedures is probably the basis for discussion on airborne transmission as against droplet transmission.
However the WHO criticised this report since the droplets were detected near where medical procedures had taken place or where droplets were generated by a nebuliser which does not reflect normal human cough conditions. The "WHO continues to recommend droplet and contact precautions", (but not nuclei aerosol precautions.)
Routes of transmission
COVID-19 is transmitted via droplets and fomites during close unprotected contact between an infector and infectee.
Airborne spread has not been reported for COVID-19, and it is not believed to be a major driver of transmission based on available evidence; however, it can be envisaged if certain aerosol-generating procedures are conducted in health care facilities.
The World Health Organisation (WHO) has also released guidelines on this, saying that airborne bioaerosol transmission of COVID-19 has not been reported, except in particular circumstances like removing a patient from a ventilator or manual ventilation.
WHO advice as at 25 May 2020. Can wearing a mask protect you against coronavirus?